
- Powershell list directory contents to file manual#
- Powershell list directory contents to file full#
- Powershell list directory contents to file code#
So, make sure you check for the file name before you create a file. Now if there was already a file with the same name, it will overwrite it. Creating files after checking for the file name In other words, this command will create an empty text file for you. Here, the Itemtype is a file, so this will create a file for you and the contents will be empty. The above command will create a new file called testfile1.txt. New-Item -Path '\\Shared\TestFolder\testfile1.txt' - ItemType File Here is how you can create a file or folder in PowerShell using the New-Item command. All that you have to do is specify the type of object you want to create in this cmdlet. In general, this cmdlet is used to create any type of object in PowerShell. To create a new file, use the New cmdlet.
In this article, we’ll be focusing on how you can create files and folders in PowerShell Creating a file
Powershell list directory contents to file manual#
In fact, it can reduce the amount of manual work associated with file management.
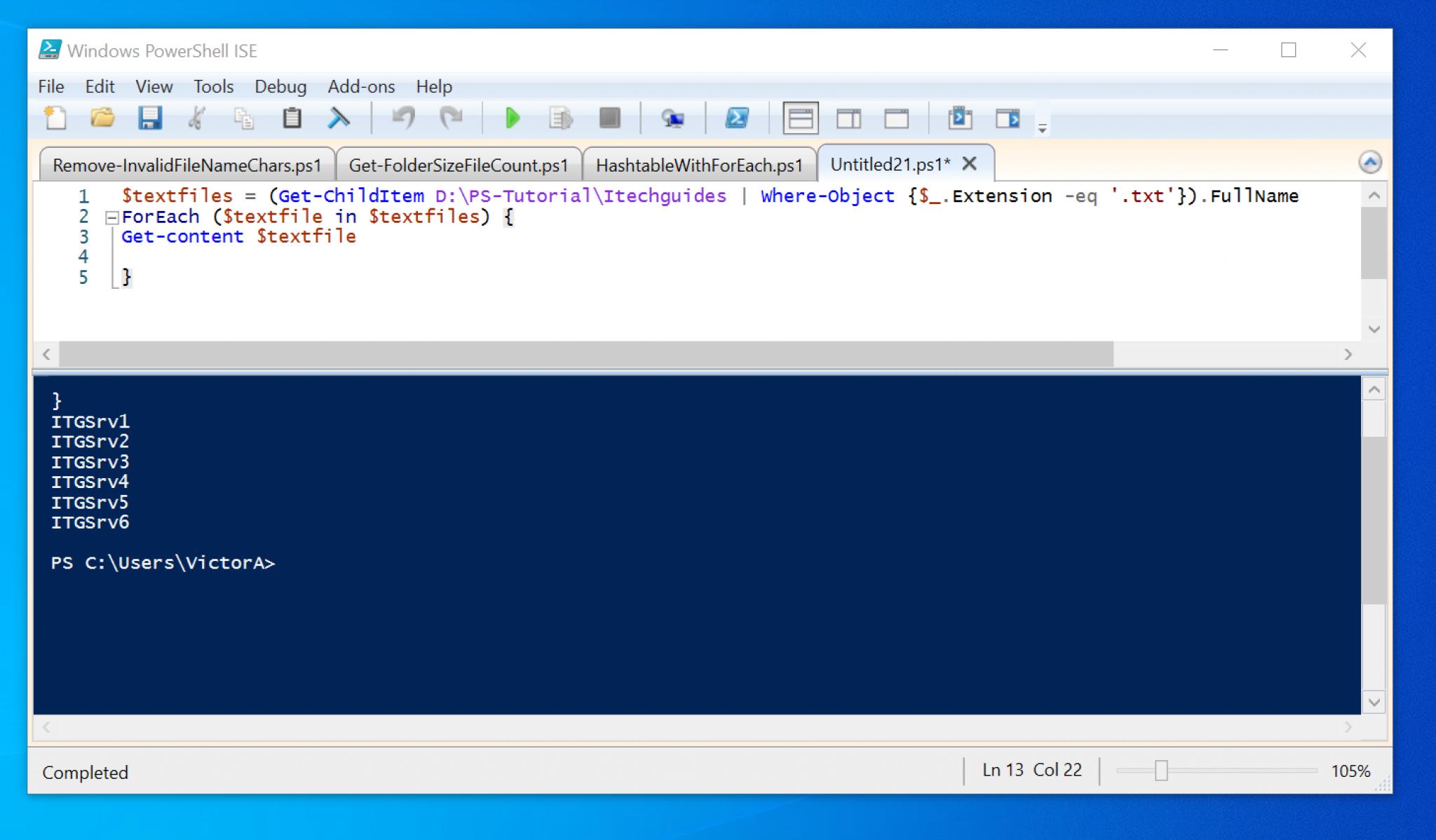
The good news is you can use PowerShell to manage files easily. If you want to specify where the CSV file is to be written, add a directory path before the file name, for example: export-csv -notypeinformation -path c:\Users\wherever\files.File management is an essential part of the everyday routine as you’ll have to manage access to shared folders, back up files and folders regularly, and do the other standard operations on files and folders in your Windows system. If you want to list all known properties for each file, change select-object FullName, LastWriteTime, Length to select-object *. If you don’t wish to conduct a recursive search, remove -Recurse and only the named folder will be searched. Alternatively, -Exclude can be used instead for the opposite purpose. In this case, I used -Include to list types of files that I did want (ie.

Powershell list directory contents to file code#
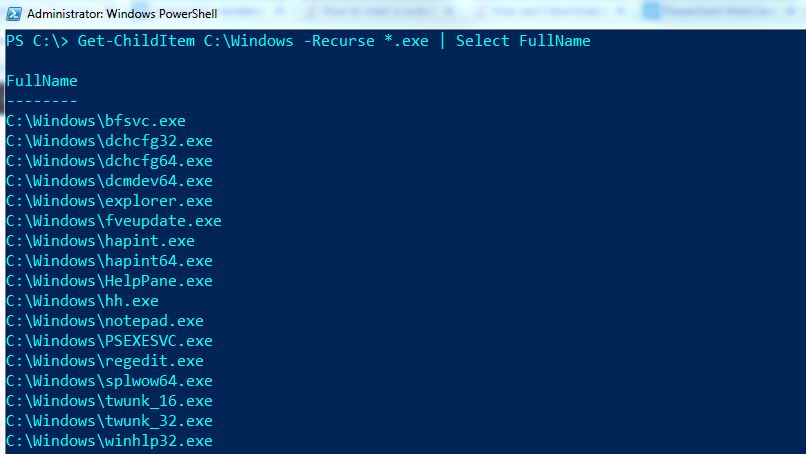
The code for this is: get-childitem c:\Users\AdamDi~1\Images\Holidays -Recurse | where
Powershell list directory contents to file full#
In this first example, I want to create an Excel comma-separated values (CSV) table of every file located within c:\Users\AdamDi~1\Images\Holidays (and its subfolders) by listing each file’s full path, the time it was last edited and its size (in bytes). Listing all files in a directory (and its subdirectories)

Instructions are available for Windows 8 and earlier versions. Starting PowerShellĪll Windows 7 and 8 machines have PowerShell installed. In order to quickly identify the largest files on the system, I put PowerShell to work and exported the results to Excel so that I could identify the largest files by size. I recently had reason to gather information about the files on my computer so that I could manage disk space. It looks a lot like Windows DOS and can work similarly.Īs one of its many functions, PowerShell can be used to collect information about the files on a computer and export that information to Excel as a tab-delimited comma-separated values file (CSV). Instructions for using a Windows PowerShell script to compile computer file data and export the results to Excel as a tab-delimited CSV.įor the uninitiated, Windows PowerShell is a DOS-like task automation and configuration management framework from Microsoft, consisting of a command-line shell and associated scripting language built on the.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
